Waveguides are one of the primary methods of efficiently carrying electromagnetic energy and RF signals from one location to another. Waveguides in particular, are extremely efficient at carrying high power signals with low loss over a considerable length. This is why the waveguide interconnect is still commonly used in high power and precision applications in the spectrum beyond 6 GHz, or millimeter-wave frequencies. As is the case with many sensing, communication, satellite communications, research/development, and test/measurement applications, there is a need to split or combine the signals traveling through different waveguide paths using Waveguide Power Dividers. This can be done with a variety of different types of power dividers/combiners, but one of the most common types is a waveguide Magic-T.
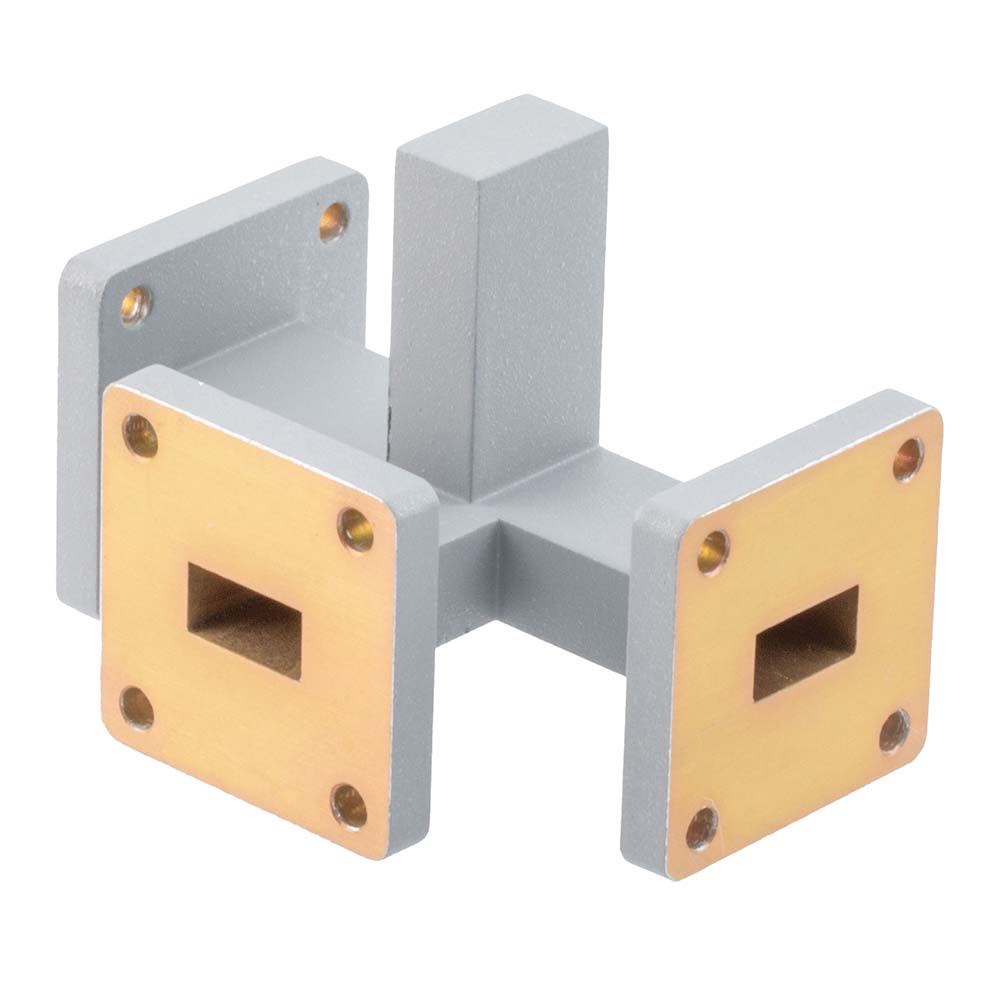
A waveguide Magic-T, or Magic Tee, is a 180-degree hybrid 4-port power divider/combiner made with a monolithic waveguide structure. The Magic Tee design has been around for over 70 years and is a merging of an H-plane waveguide arm meeting with an E-plane waveguide arm at a junction along with two collinear ports. The effect of a Magic Tee is that if two signals are injected into the collinear ports, then the combination of the two signals exit the H-plane port and the difference of the two signals exits the E-plane port. If a signal is injected into the H-plane port then the signals are divided equally to the outputs of the two collinear ports with no energy output at the E-plane port. Lastly, if the signal is injected into the E-plane port then the signal energy is divided between the two collinear ports, except that the signals at the collinear port outputs are 180-degree opposite in phase with no signal energy output at the H-plane port.
This behavior often leads to a nomenclature that calls the H-plane port the Sum port and the E-plane port the Difference port. Ideally, a Magic-Tee has no loss, absolute isolation among the ports, and perfect phase balance among the ports. Given machining tolerances, plating tolerances, etc, there are imperfections in the waveguide power divider/combiner that lead to impedance imbalances (VSWR) among the ports and phase imbalances. These are typically specified as amplitude balance and phase balance between the two collinear ports. There is also loss within a Magic-Tee that is the sum of the power loss between the input port and the output ports of the Magic-T. As a function of the imbalances, there is also inevitably some energy that escapes the E-plane and H-plane ports when they are not intentionally stimulated (isolation).


